The close of each calendar year brings with it the holidays as well as a chance to look forward to the year ahead. In the coming weeks, investors are likely to be bombarded with predictions about what the future, and specifically the next year, may hold for their portfolios. These outlooks are typically accompanied by recommended investment strategies and actions that are aimed at trying to avoid the next crisis or missing out on the next “great” opportunity. When faced with recommendations of this sort, it would be wise to remember that investors are better served by sticking with a long-term plan rather than changing course in reaction to predictions and short-term calls.
Predictions & Portfolios
One doesn’t typically see a forecast that says: “Capital markets are expected to continue to function normally,” or “It’s unclear how unknown future events will impact prices.” Predictions about future price movements come in all shapes and sizes, but most of them tempt the investor into playing a game of outguessing the market. Examples of predictions like this might include: “We don’t like energy stocks in 2017,” or “We expect the interest rate environment to remain challenging in the coming year.” Bold predictions may pique interest, but their usefulness in application to an investment plan is less clear. Steve Forbes, the publisher of Forbes Magazine, once remarked, “You make more money selling advice than following it. It’s one of the things we count on in the magazine business—along with the short memory of our readers.”1 Definitive recommendations attempting to identify value not currently reflected in market prices may provide investors with a sense of confidence about the future, but how accurate do these predictions have to be in order to be useful?
Consider a simple example where an investor hears a prediction that equities are currently priced “too high,” and now is a better time to hold cash. If we say that the prediction has a 50% chance of being accurate (equities underperform cash over some period of time), does that mean the investor has a 50% chance of being better off? What is crucial to remember is that any market-timing decision is actually two decisions. If the investor decides to change their allocation, selling equities in this case, they have decided to get out of the market, but they also must determine when to get back in. If we assign a 50% probability of the investor getting each decision right, that would give them a one-in-four chance of being better off overall. We can increase the chances of the investor being right to 70% for each decision, and the odds of them being better off are still shy of 50%. Still no better than a coin flip. You can apply this same logic to decisions within asset classes, such as whether to currently be invested in stocks only in your home market vs. those abroad. The lesson here is that the only guarantee for investors making market-timing decisions is that they will incur additional transactions costs due to frequent buying and selling.
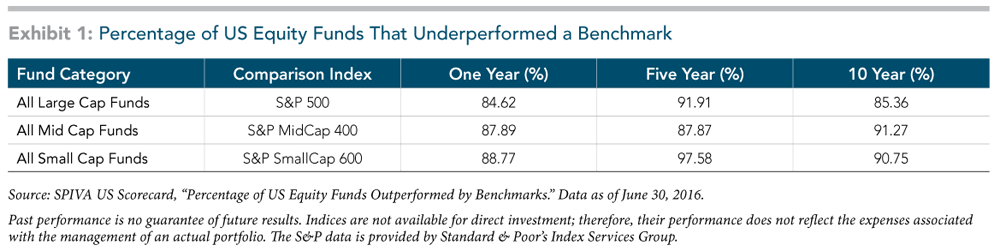
The track record of professional money managers attempting to profit from mispricing also suggests that making frequent investment changes based on market calls may be more harmful than helpful. Exhibit 1, which shows S&P’s SPIVA Scorecard from midyear 2016, highlights how managers have fared against a comparative S&P benchmark. The results illustrate that the majority of managers have underperformed over both short and longer horizons.
Rather than relying on forecasts that attempt to outguess market prices, investors can instead rely on the power of the market as an effective information processing machine to help structure their investment portfolios. Financial markets involve the interaction of millions of willing buyers and sellers. The prices they set provide positive expected returns every day. While realized returns may end up being different than expected returns, any such difference is unknown and unpredictable in advance.
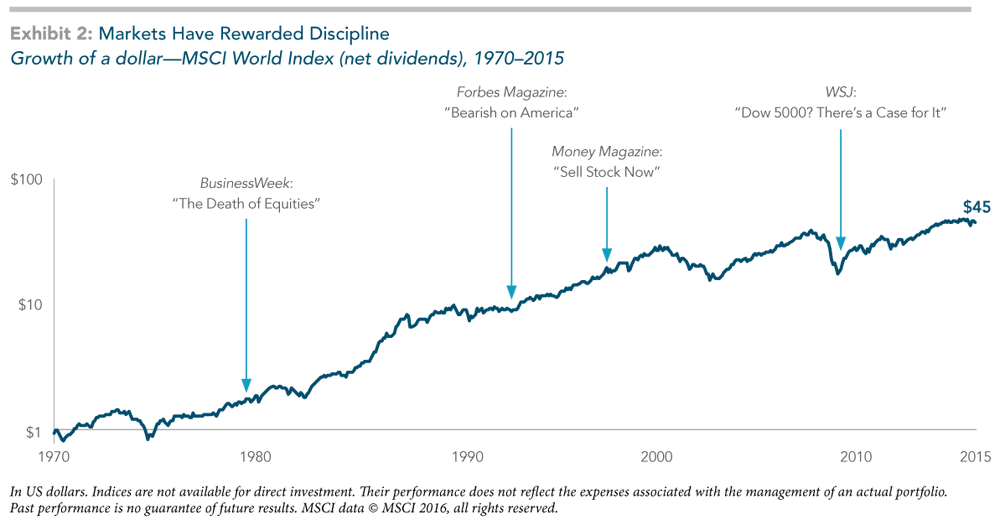
Over a long-term horizon, the case for trusting in markets and for discipline in being able to stay invested is clear. Exhibit 2 shows the growth of a US dollar invested in the equity markets from 1970 through 2015 and highlights a sample of several bearish headlines over the same period. Had one reacted negatively to these headlines, they would have potentially missed out on substantial growth over the coming decades.
Conclusion
As the end of the year approaches, it is natural to reflect on what has gone well this year and what one may want to improve upon next year. Within the context of an investment plan, it is important to remember that investors are likely better served by trusting the plan they have put in place and focusing on what they can control, such as diversifying broadly, minimizing taxes, and reducing costs and turnover. Those who make changes to a long-term investment strategy based on short-term noise and predictions may be disappointed by the outcome. In the end, the only certain prediction about markets is that the future will remain full of uncertainty. History has shown us, however, that through this uncertainty, markets have rewarded long-term investors who are able to stay the course.



